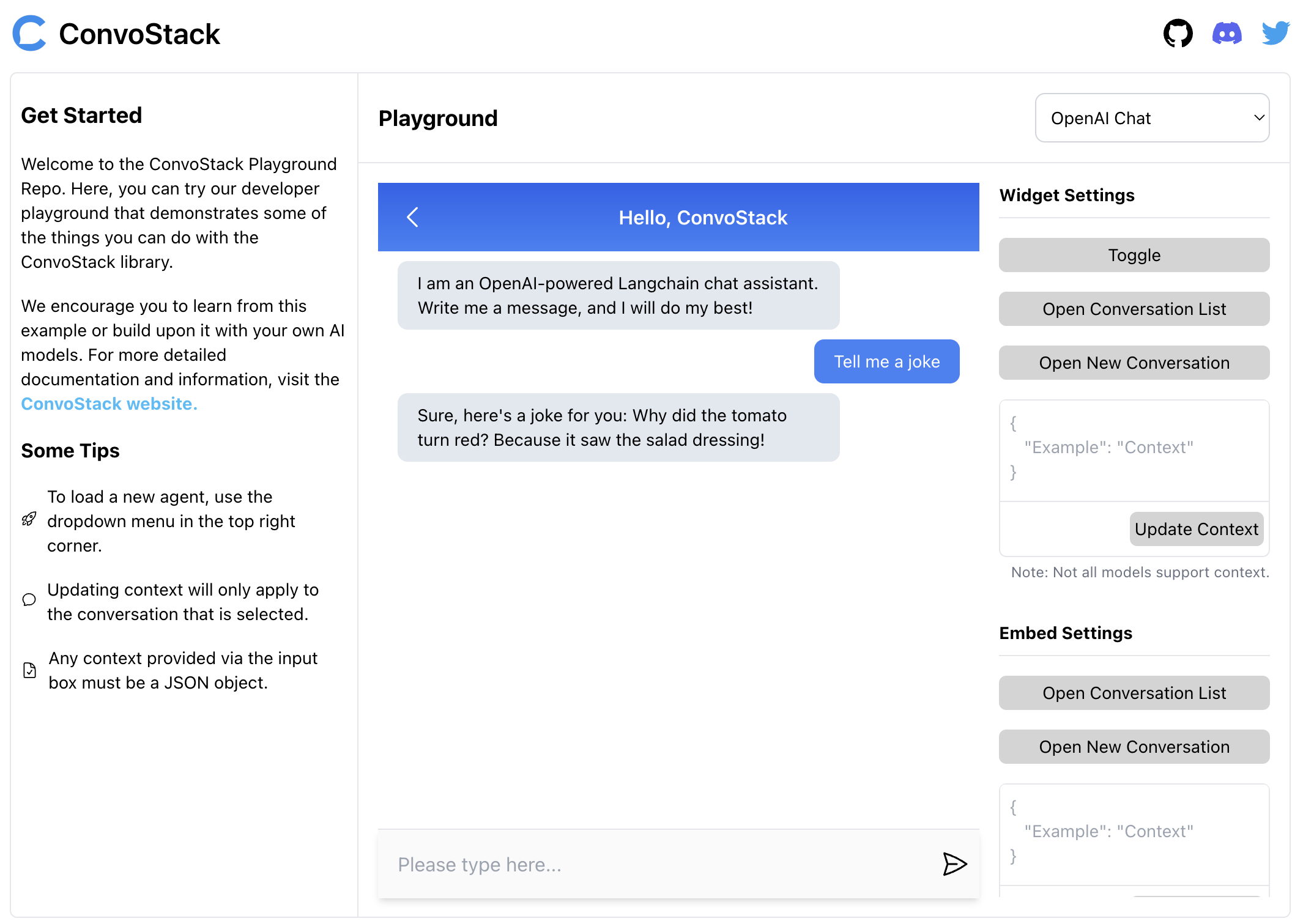
Playground Repository
To check out the playground without setting it up yourself, click here for a live demo!
By following this guide, you will end up with a runnable local version on your own machine. We estimate that you can go from git clone to running in a couple of minutes. If you don't want to read the details of each step, you can copy/paste the steps directly from the GitHub repo README.
Requirements & Installation
To get started, clone the ConvoStack playground monorepo:
# Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/ConvoStack/playground convostack-playground
# Enter the project root directory
cd convostack-playground
From the root of the monorepo, let's install our dependencies:
# Install all dependencies
npm install
Environment Setup
To load environment variables from a .env file in the apps/backend directory, the playground utilizes dotenv.
You are not required to customize any parameters to run the playground, but you will need to copy the .env.example
file over to .env to get it up and running:
# Setup your backend .env using the example provided
# Optionally, edit the apps/backend/.env file to set your OpenAI and/or Pinecone API keys to try some of the more advanced demos
cd apps/backend
cp .env.example .env
Database Migrations
ConvoStack requires a persistent storage engine that implements convostack/models.IStorageEngine in order to work.
Conveniently, ConvoStack comes with pre-built implementations of IStorageEngine so that you don't need to write any
boilerplate database code.
The default storage backend for the playground is SQLite, which means you don't need to run any databases yourself to
run the playground. However, we will still need to run migrations to setup the SQLite .db file:
# **Make sure that you're still in the apps/backend directory** #
# Run the SQLite migrations
npm run migrate-sqlite
Running locally
Now that we have installed and set up our environment and database, we can locally run our playground application:
# Get back into the root of the project. If you were running migrations earlier, run:
cd ../..
# Start the full-stack demo from the root of the project
npm run dev
# 🚀 See the demo running now on http://localhost:5173/ (GraphQL server on http://localhost:3000/graphql)
And there we have it...the ConvoStack playground is running locally on your own machine!
Monorepo Overview
Up until now, we have setup and used an implementation of ConvoStack to power our playground.
To understand how this all magically works, we are going to dive into the key elements of the Convostack backend and frontend frameworks which the playground monorepo implements.
Backend Framework (source)
The ConvoStack backend framework offers several key features and options for easy development and setup:
- Database Support:
- For development, ConvoStack supports SQLite for convenient setup and local testing.
- For production, you have the flexibility to choose between Postgres and MySQL, ensuring compatibility with your preferred database system.
- Caching and Pub/Sub:
- For development, ConvoStack provides in-memory caching and pub/sub capabilities, enabling efficient data management and real-time communication.
- For production, ConvoStack supports Redis, a widely-used caching and message broker system.
- Multiple AI Agent Implementations:
- ConvoStack offers various "agent" implementations to suit different use cases (all four are built and running in
the playground). These include:
- "OpenAI Chat": an agent powered by OpenAI and Langchain that operates like the popular ChatGPT application.
- Requires
OPENAI_API_KEYto be set
- Requires
- "Echo Agent": a super-simple agent that showcases a minimalistic ConvoStack implementation with no API keys required.
- "OpenAI Conversational QA": an agent powered by OpenAI and Langchain for question and answering given various
sources.
- Requires
OPENAI_API_KEYto be set
- Requires
- "ConvoStack Docs Agent": a web crawler and chat QA chain based on Pinecone, OpenAI, and Langchain, which is
production-ready for powering chat with your documentation or help center. Powers chat
on ConvoStack.ai and this docs site!
- Requires
OPENAI_API_KEY,PINECONE_API_KEY,PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT, andPINECONE_INDEXto be set - Loading the documents requires running the following
npm run pinecone-load-convostack-docscommand in theapps/backenddirectory to crawl the ConvoStack docs website and load the embeddings into Pinecone. Make sure that you have created an index on Pinecone using dimension=1536 and the cosine distance function and updated your backend.envwith the required env vars listed above.
- Requires
- "OpenAI Chat": an agent powered by OpenAI and Langchain that operates like the popular ChatGPT application.
- ConvoStack offers various "agent" implementations to suit different use cases (all four are built and running in
the playground). These include:
- Deployment with Fly.io:
- ConvoStack deploys seamlessly to Fly.io, providing free and easy hosting options. The included
fly.tomlfile simplifies the deployment configuration process.
- ConvoStack deploys seamlessly to Fly.io, providing free and easy hosting options. The included
- Optional Docker Configuration:
- ConvoStack offers an optional
docker-compose.ymlconfiguration for local development using Postgres, MySQL, and Redis. This facilitates a consistent development environment that closely mirrors the production setup.
- ConvoStack offers an optional
By leveraging these features provided by the ConvoStack backend framework, you can efficiently develop and deploy chatbot applications with ease. The framework's flexibility, database support, caching capabilities, agent implementations, and hosting options make it a powerful choice for building conversational experiences.
Frontend Framework (source)
The ConvoStack frontend framework, powered by React, offers out-of-the-box AI chatbot components that connect to your backend:
- Core React Components:
- The Widget: like the one running on ConvoStack.ai and this docs site! Customizable via
the
CustomStylingprop. - Embeddable Chat: can be embedded on any page of your website. Also customizable via the
CustomEmbedStylingprop.
- The Widget: like the one running on ConvoStack.ai and this docs site! Customizable via
the
- useConvoStack Hook:
- The framework provides an exported
useConvoStackhook that offers functions enabling GraphQL API calls and component state management. - This hook simplifies interaction with the ConvoStack backend, facilitating seamless communication and efficient state management within the chatbot interface.
- The framework provides an exported
- User Data Integration:
- By default, the ConvoStack frontend framework does not persist login data. Conversations will be cleared upon reloading the page.
- If desired, you can customize the
ConvoStackWidgetconfiguration inapps/frontend/src/main.tsxusing theuserDataprop to enable data persistence between sessions or even hardcode a demo user for development purposes.
- Vite for Bundling:
- The ConvoStack frontend framework utilizes Vite as the bundler. Vite is a fast and efficient build tool that enhances development speed and optimizes the performance of the chatbot application.
- Simplified Hosting:
- The build script of the ConvoStack frontend framework exports to the backend server, eliminating the need for separate static site hosting. This streamlined approach simplifies the deployment process, allowing for a single hosting solution for both the frontend and backend components of the ConvoStack application.
Monorepo Project Structure
The playground monorepo is organized into two distinct applications in the apps workspace: apps/backend
and apps/frontend.
Backend Folder
- The ConvoStack backend is initialized in the
apps/backend/src/server.tsfile- The agents are connected to the backend in this file
- The Express server is defined here
- All ConvoStack agent implementations live in the
apps/backend/src/agentsdirectory- All agent logic lives in the agent files
- There are no limitations on what frameworks and resources a ConvoStack agent can use, as long as it
implements the
replymethod ofconvostack/agent.IAgent
Frontend Folder
- The
ConvoStackWrapperandConvoStackWidgetcomponents are initialized in theapps/frontend/src/App.tsxfile- The
graphqlUrl,websocket, andcustomStylingprop values are defined here
- The
- The
ConvoStackEmbedcomponents anduseConvoStackhook are initialized in theMobilePlayground.tsxandWebPlayground.tsxcomponents- The
useConvoStackhook is also utilized in theContextInput.tsxfile
- The
Monorepo folder structure
./
├── apps/ # Monorepo apps workspace
│ ├── backend/ # Typescript Express server
│ │ ├── mysql-storage/... # Auto-generated MySQL Storage Backend migrations, schema, etc.
│ │ ├── postgres-storage/... # Auto-generated Postgres Storage Backend migrations, schema, etc.
│ │ ├── sqlite-storage/... # Auto-generated SQLite Storage Backend migrations, schema, etc.
│ │ ├── scripts/... # Data loading and utility scripts
│ │ ├── datasets/... # Demo data for the various agents
│ │ ├── src/ # Express server source
│ │ │ ├── agents/... # ConvoStack agents for playground demos
│ │ │ ├── utils/... # Server and agent utils
│ │ │ └── server.ts # Server entrypoint <--- ConvoStackBackendExpress is configured and initialized here
│ │ ├── Dockerfile # Production deployment Dockerfile (compatible with Fly.io)
│ │ ├── fly.toml # Fly.io deployment spec
│ │ ├── package.json # Server dependencies and scripts
│ │ └── tsconfig.json # Server TypeScript config
│ └── frontend/ # TypeScript React Client
│ ├── public/... # Public assets
│ ├── src/ # React client source
│ │ ├── api/... # Playground configuration API
│ │ ├── components/... # Playground React components
│ │ ├── types/... # Playground types
│ │ ├── App.tsx # React app component
│ │ ├── index.css # Playground client styles
│ │ ├── main.tsx # Client entrypoint <--- ConvoStackWrapper is configured and initialized here
│ ├── index.html # Client base index.html file
│ ├── package.json # Client dependencies and scripts
│ ├── postcss.config.js # PostCSS config
│ ├── tailwind.config.js # Tailwind config
│ ├── tsconfig.json # Client (browser) TypeScript config
│ ├── tsconfig.node.json # Client (node) TypeScript config
│ └── vite.config.ts # Vite config
├── docker-compose.yml # Optional Postgres, MySQL, and Redis docker-compose local configuration
├── package.json # Monorepo package.json configuration, dependencies, and global scripts
└── turbo.json # Monorepo (Turbo) configuration and global scripts